Sun, Jul 20, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 2 (JUNE 2025)
IJMSE 2025, 22(2): 58-65 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Fawzy Z D, Muhsin S A, Abood T H. In Vitro Evaluation of Ceramic-Amber Hardness Supported Zirconia. IJMSE 2025; 22 (2) :58-65
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3836-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3836-en.html
Abstract: (4349 Views)
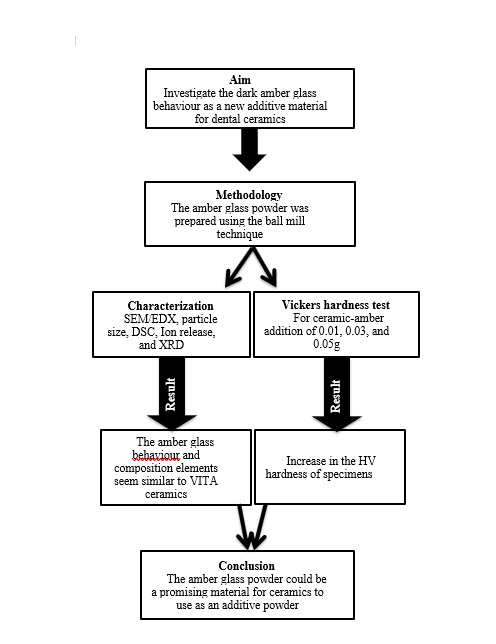
Ceramics in dentistry have been mainly recommended from a cosmetic perspective. Yet, the hardness behaviour may limit the application in many cases. Although amber glass is used for medications and chemicals, no studies focus on using amber glass for dental purposes as an additive material. This study aims to investigate the dark amber glass behaviour as a new additive material for dental ceramics. The amber glass powder was prepared using the ball mill technique. For the amber glass powder characterization, the SEM/EDX, particle size, DSC, Ion release, and XRD analysis were tested compared to VITA Lumex® AC ceramic. In addition, the Vickers hardness test was applied for ceramic and ceramic amber with an addition of 0.01g, 0.03g, and 0.05g amber glass powder following the DIN EN ISO 6872/ 2019. Statistically, the ANOVA (post hoc- Tukey) test was used for hardness testing analysis at a significant P-value of (P≤0.05). The results show that the amber glass behaviour and composition elements seem similar to VITA ceramics. The addition of amber glass powder to ceramic shows an increase in the HV hardness of specimens. Overall, it was concluded that the amber glass powder could be a promising material for ceramics to use as an additive powder.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Ceramic Materials and Engineering
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |