Thu, Feb 19, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 1 (March 2025)
IJMSE 2025, 22(1): 85-98 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Bali Chalandar A, Farnia A, Najafi H, Jafarian H R. Effect of Pre-cold Deformation and Welding Current Mode on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of GTAWed Nimonic 80A Superalloy. IJMSE 2025; 22 (1) :85-98
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3821-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3821-en.html
Abstract: (14710 Views)
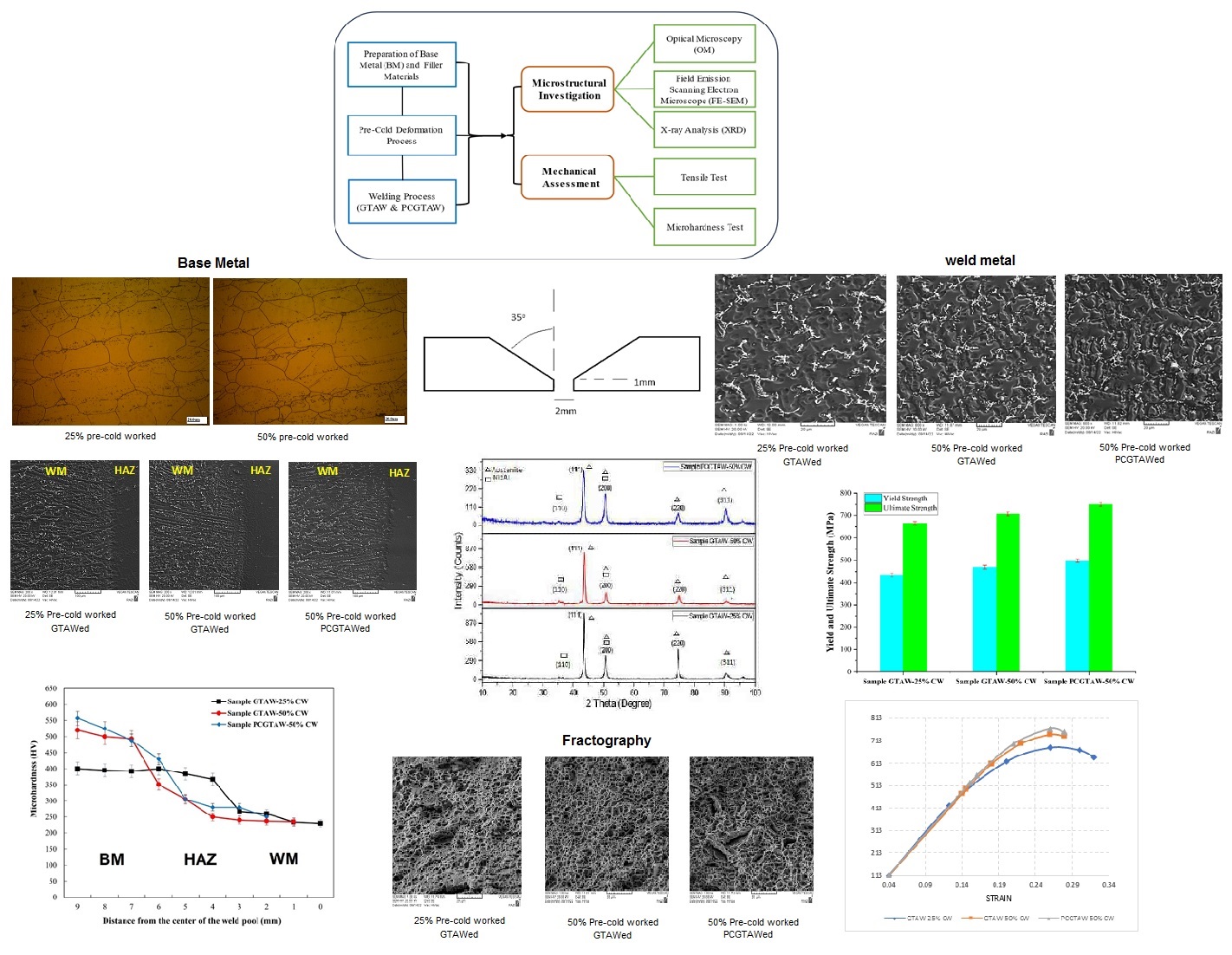
This study investigates the microstructural evolution and variations in the mechanical properties of pre-cold worked Nimonic 80A superalloy, subjected to two levels of deformation (25% and 50%) and welded via Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) and Pulsed Current Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (PCGTAW) techniques using ER309L filler wire. The objective is to evaluate the effect of the initial microstructure on the welding behavior of Nimonic 80A and compare the weldments produced using GTAW and PCGTAW. Microstructural characterization was conducted using optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). XRD analysis demonstrated that the welding pulsed current mode, compared to the continuous current mode and at equal heat input, led to a refined microstructure, suggesting improved welded mechanical properties of the weld. It also showed a potential reduction in grain refinement with a higher level of cold work. Tensile testing demonstrated that fractures consistently occurred within the weld zone (WZ), with the PCGTAW sample achieving the highest tensile strength (766 MPa). Microhardness analysis indicated a notable reduction in hardness within the heat-affected zone (HAZ) and WZ, particularly in the 50% pre-cold worked sample. However, PCGTAW retained higher hardness due to its refined microstructure. The weld metal primarily consisted of an austenitic microstructure characterized by dendrites and interdendritic precipitates. Microstructural analysis revealed that welding induced significant changes in the weldment, with the PCGTAW sample exhibiting a more uniform microstructure and smoother transitions at the weld interface. Fractography confirmed ductile fracture in all specimens, with smoother and more uniformly distributed dimples in the PCGTAW sample. These findings highlight the advantages of pulsed current welding in optimizing the mechanical performance of Nimonic 80A welds and suggest its potential application in industries requiring superior weld quality.
Keywords: Nimonic 80A Superalloy, GTAW Welding, Pre-Cold Worked, Initial Microstructure, PCGTAW Process.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |