Wed, Oct 22, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 2 (JUNE 2025)
IJMSE 2025, 22(2): 32-48 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mopoung S, Seeoon K. Development of Porous Character in Tamarind Wood Derived Charcoal by Microwave-Assisted Sodium Chloride Activation for Methylene Blue Adsorption. IJMSE 2025; 22 (2) :32-48
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3647-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3647-en.html
Abstract: (8842 Views)
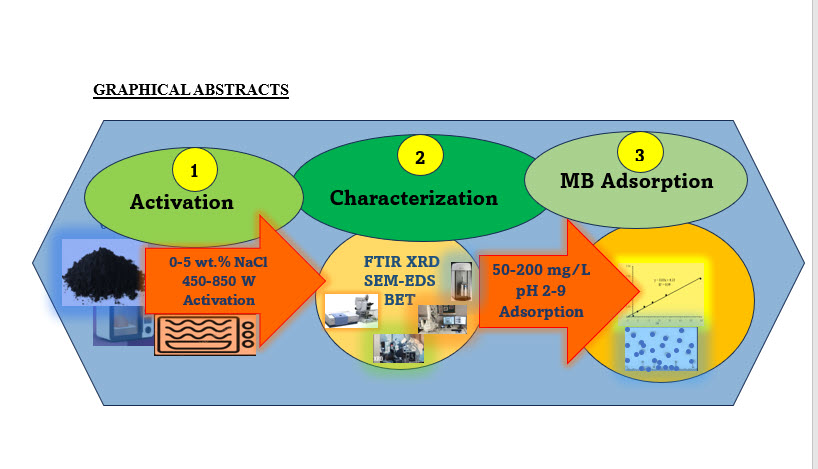
Activated carbon preparation from tamarind wood derived charcoal by microwave-assisted sodium chloride activation was studied to investigate the effects of 0-5 wt.% NaCl and 450-850 W microwave heating power. The properties of the derived products were analyzed by FTIR, XRD, SEM-EDS, and BET. Methylene blue adsorption by the activated carbon products was also studied to evaluate the contract time, pH, methylene blue concentration, and adsorption isotherms. The study’s results showed that the percent yields (77.42-92.52%) of the fabricated activated carbons decrease with increasing wt.% of NaCl and MP. On the other hand, the contents of disordered graphitic carbon, carbonate, basic surface functional groups, and mesopores increased. However, 3 wt.% NaCl and 600 W microwave irradiation power were identified as appropriate conditions for activation, which created the micro-mesopore (pore size range 1.59 -14.76 nm) on the surface of the derived activated carbon products. Optimal values of equilibrium time and pH for methylene blue adsorption are 60 minutes and 8, respectively. The results of methylene blue concentrations were fitted to the Langmuir isotherm indicating 33.33 mg/g as the maximum methylene blue adsorption capacity.
Keywords: tamarind wood charcoal, activated carbon, sodium chloride, methylene blue, Microwave irradiation
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Ceramic Materials and Engineering
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |